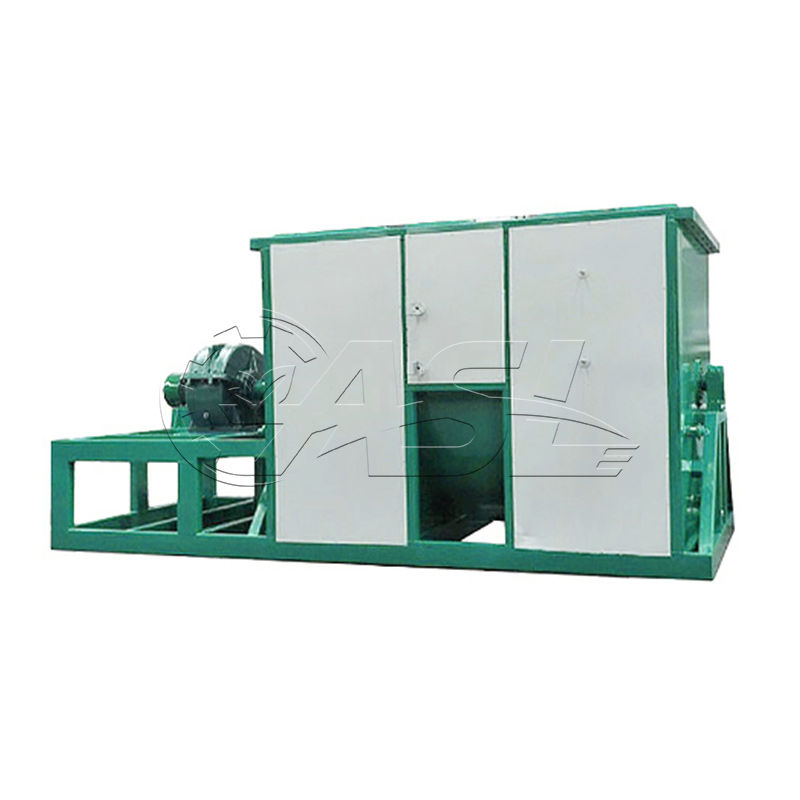
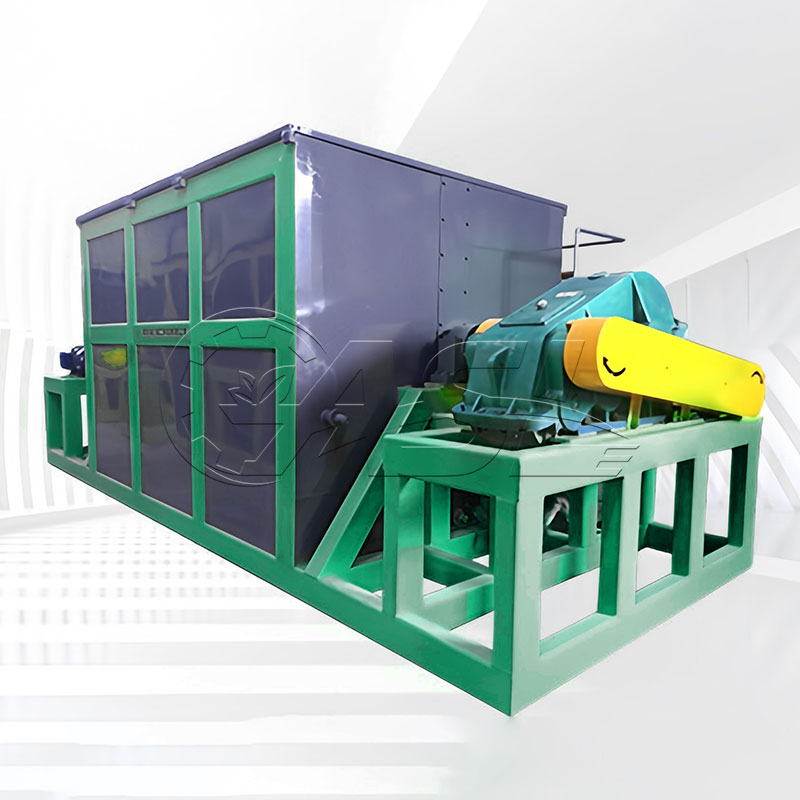
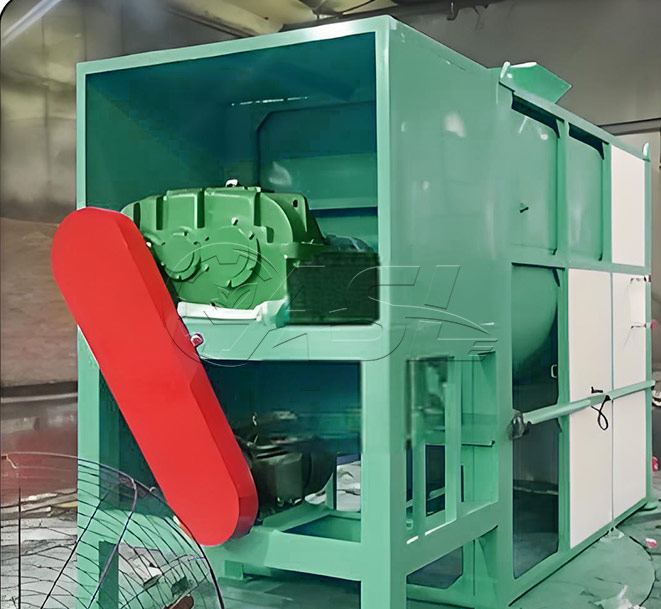
What materials are suitable for fermenting in horizontal organic fertilizer fermentation tanks?
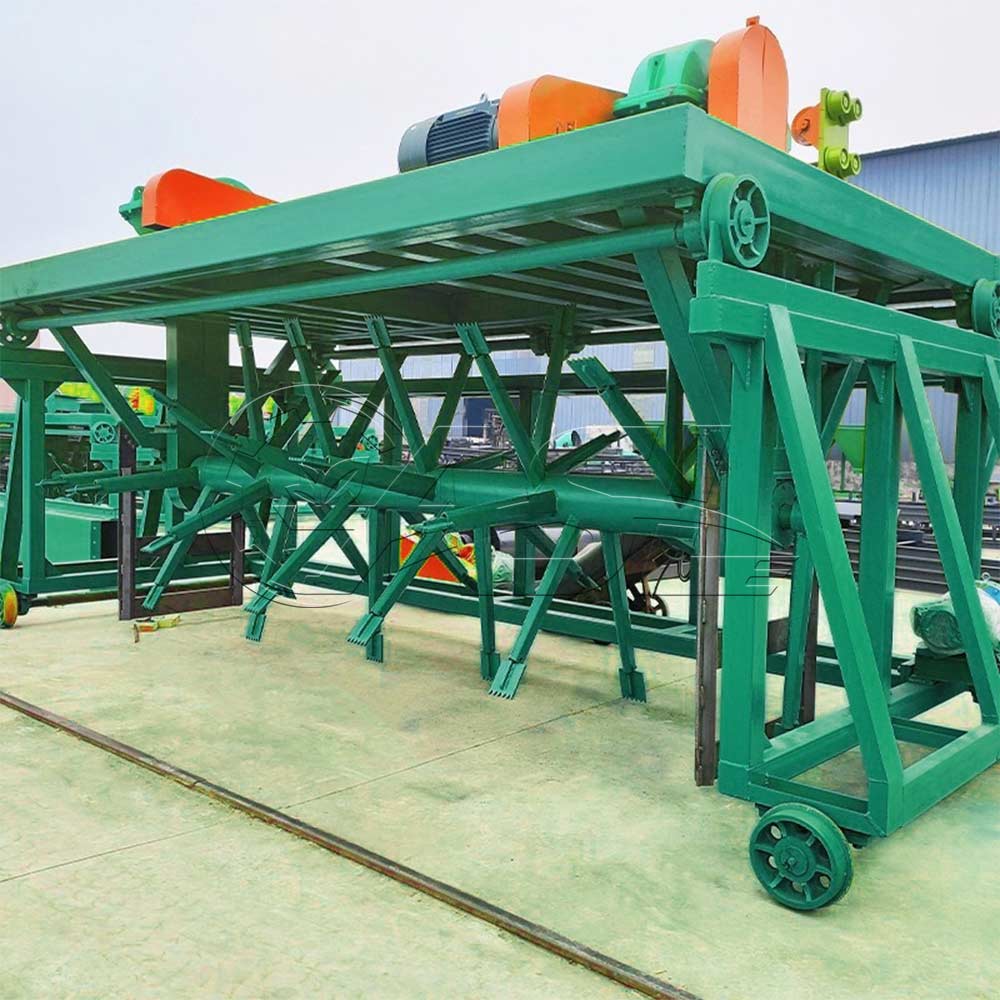
Horizontal organic fertilizer fermentation tanks are suitable for a variety of organic waste materials, including livestock and poultry manure, crop straw, food waste, sludge, fungal residue, and medicinal residue. They are particularly suitable for processing materials with high moisture content, such as fresh manure from livestock farms and municipal sludge. The tank's internal stirring and temperature control system effectively prevents the clumping and poor air permeability problems that these materials often encounter during fermentation.
What are the advantages of horizontal fermentation tanks compared to vertical fermentation tanks?
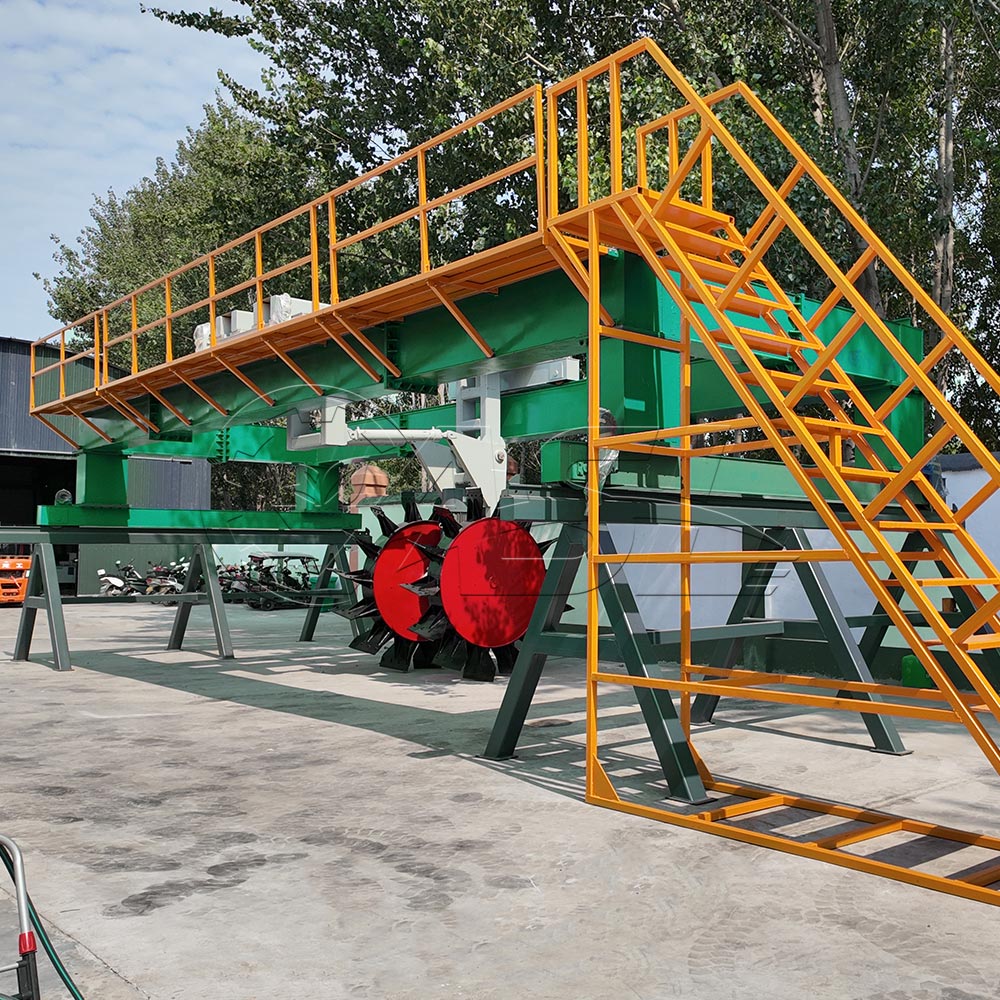
The advantages of horizontal fermentation tanks primarily lie in uniform material handling and footprint. The horizontal structure allows the stirring device to more fully contact the material, avoiding the uneven fermentation between the upper and lower layers of the material caused by gravity in vertical tanks. Horizontal tanks are typically longer than they are high, resulting in a more compact footprint and suitable for sites with ample horizontal space. Furthermore, horizontal tanks offer easier loading and unloading, enabling continuous feeding and discharging through openings at the ends or sides, making them suitable for large-scale continuous production.
What is the typical fermentation cycle of a horizontal fermentation tank?
The fermentation cycle is affected by the material properties, tank temperature, and agitation frequency. Under ideal conditions (temperature of 55-65°C, adequate agitation, and sufficient oxygen), the fermentation cycle for livestock and poultry manure is typically 7-10 days; high-fiber materials such as straw may require 10-15 days. Compared to open-air composting (30-60 days), horizontal fermenters, due to their controlled environment, can shorten the fermentation cycle by over 50%, achieving rapid material maturity.
Is operating a horizontal fermenter difficult? Do they require specialized technicians?
Modern horizontal fermenters are often equipped with automated control systems that monitor parameters such as tank temperature, humidity, and oxygen content in real time, and automatically adjust agitation frequency, ventilation, and heating levels. Operation is relatively simple. Operators only need to perform startup, parameter setting, and routine inspections. Basic operation can be mastered after 1-2 days of training. However, equipment maintenance (such as overhauling the agitation system and calibrating sensors) may require technicians with sufficient mechanical and electrical knowledge.
What safety precautions should be taken when using a horizontal fermenter?
During operation, please note the following:
① Before adding materials, ensure that there are no hard objects such as metal or stones in the material to avoid damage to the agitator.
② During fermentation, methane and other gases may be generated in the tank. Ensure the ventilation system is functioning properly to prevent gas accumulation and explosion.
③ During maintenance, the power must be disconnected and warning signs must be displayed to prevent accidental startup.
④ During high-temperature fermentation, the tank surface temperature may be high; prevent burns.
⑤ Regularly check safety devices such as safety valves and pressure gauges to ensure they are sensitive and reliable.
What are the key points for maintenance of horizontal fermenters?
Daily maintenance needs to focus on the following:
① Agitation system: Regularly check the agitator paddles for wear, tighten the connecting bolts, and add lubricant.
② Sealing system: Check the seals at both ends of the tank for wear to prevent material leakage.
③ Electrical system: Clean the control panel, check the wiring connections, and ensure that the sensors and control system are functioning properly.
④ Ventilation system: Clean the filter to ensure smooth ventilation and avoid blockage.
⑤ Regularly treat the tank for corrosion to extend its service life.